We are pleased to announce that over 20,000 pages of lecture notes and related material has been digitized to date as part of “For the Health of the New Nation” grant. “For the Health of the New Nation: Philadelphia as the Center of American Medical Education, 1746-1868” is a two-year project funded by CLIR and organized by the Philadelphia Area Consortium for Special Collections Libraries (PACSCL). The initiative will digitize, describe, and provide access to 140,000 pages of lecture tickets, course schedules, theses, dissertations, student notes, faculty lectures notes, commencement addresses, opening addresses, and matriculation records, sharing not only the voices of the medical greats, but also the often unheard voices of students.
Digitization
If You Build it, They Will Come (And Maybe They Will Read It Too)
Since starting as Digital Projects Librarian here at the Historical Medical Library of the College of Physicians of Philadelphia, one of my jobs has been to create new interpretive online exhibitions featuring unique aspects of our collections. Digital exhibitions are a great way to bring life to collections and to promote your institution. However, many exhibitions based on just text and images fail to be engaging in our age of constant clicking and easy distraction.
A plethora of articles exist showing that people do not engage with text online the same way they might if they were reading a book or a print article. Simply type “how people read online” into your favorite search engine and you’ll see headlines like, “How People Read Online: Why You Won’t Finish This Article” from Salon, or “Myth #1: People Read Online,” from the user design blog UXMyths. Indeed, a study by Jakob Nielsen, a prominent web usability expert, which tracked readers eyes as they read online, showed that only about 20% of the words of an average online text were actually being read. Studies like this show that online readers scan and click.
If you or your institution are going to be putting the time and effort into creating digital content around your collections, it is worth thinking about how to create digital exhibitions catered to people’s online behavior. Luckily, people in the digital humanities world have been thinking about this problem and have created tools for content creators to more easily build interactive and engaging exhibitions. I will be highlighting two such tools that I used in the creation of our last two major digital exhibitions.
Seeing is Believing: Ophthalmology Over the Ages
We have all heard the phrase “an eye for an eye.” The full passage, from The Code of Hammurabi, 2250 B.C.E., reads, “If a man destroy the eye of another man, they shall destroy his eye.” Less well known are the other ocular codes, including, “If a physician open an abscess (in the eye) of a man with a bronze lancet and destroy the man’s eye, they shall cut off his fingers.”
Ophthalmology, in a way, thus existed in ancient Babylon, meaning that the field is over 4,000 years old. Indeed, the ancient Egyptians detailed the treatment of cataracts and trachoma in papyri dating to 1650 B.C.E.
Hippocrates, the father of all medicine who lived in Greece in 5th century B.C.E., knew of the optic nerve, though he did not understand its function. He described many treatments for maladies of the eye, including restricted diets, hot footbaths and even cutting incisions into the scalp to excise the “morbid humors” of the eye. Galen, whose influence on Western medicine through the 18th century cannot be overstated, wrote two volumes related to ophthalmology, both of which are lost to history. However, his Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye exists to this day and prevailed for nearly 1,500 years after his death in 210 C.E.
“Look” Out for Our New Series: Seeing is Believing
As the medievalists among you probably know, #MedievalMondays has drawn to a close. This new blog series, Seeing is Believing, is one of two that will be taking its place. (Stay tuned next month as Caitlin Angelone, our Reference Librarian and Queen of Pamphlets, introduces you to some of our trade ephemera.)
Every other month, I will be scouring our collection for thematically linked material that is interesting to read about but is also interesting to look at. As such, what more fitting topic could be chosen for the inaugural month than the eye, the very vessel of seeing.
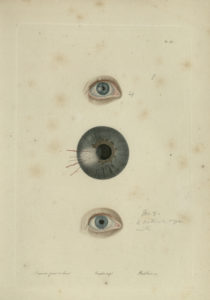
Stay tuned to this blog for the introductory post to this month’s topic next Monday 2/2/2018, and follow us on Twitter @CPPHistMedLib where each week this month I will be adding to this brief history of ophthalmology by posting a new image with a link to the full metadata in our Digital Library.
Vale
Over the past 11 months, we have examined the College’s collection of all things medieval: manuscripts, incunabula bound in manuscript waste, and uncatalogued documents. Features of our medieval materials that I’ve written about include catchwords, ink (here and here), illuminations (here, here, and here), scripts (here, here, here, and here), and parchment. But what’s the point? Why study these books, leaves, and documents that are over 500 years old?

Medicine at Ground Level: Digitizing State Medical Journals with the Medical Heritage Library
As part of its partnership with the Medical Heritage Library, the Historical Medical Library (HML) of the College of Physicians of Philadelphia has completed a National Endowment for the Humanities-funded initiative Medicine at Ground Level: State Medical Societies, State Medical Journals, and the Development of American Medicine, 1900-2000.
The Medical Heritage Library has released 3,907 state medical society journal volumes free of charge for nearly 50 state medical societies, including those for the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico, through the Internet Archive (http://www.medicalheritage.org/content/state-medical-society-journals/). The journals – collectively held and digitized by Medical Heritage Library founders and principal contributors The College of Physicians of Philadelphia; the Center for the History of Medicine, Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine; The New York Academy of Medicine Library; the Library and Center for Knowledge Management at the University of California at San Francisco; the National Library of Medicine of the National Institutes of Health; the Augustus C. Long Health Sciences Library at Columbia University and Columbia University Libraries; and content contributor the Health Sciences and Human Services Library, University of Maryland, Founding Campus, with supplemental journal content provided by the Brown University Library, the Health Sciences Library of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the University of Pittsburgh Health Sciences Library System, and UT Southwestern Medical Center Health Sciences Digital Library and Learning Center – consist of almost three million pages that can be searched online and downloaded in a variety of formats.
Making the Medieval Digital
“If [medieval] culture is regarded as a response to the environment then the elements in that environment to which it responded most vigorously were manuscripts.”
– C. S. Lewis, The Discarded Image: An Introduction to Medieval and Renaissance Literature

The Historical Medical Library, as part of the Philadelphia Area Consortium of Special Collections Libraries (PACSCL), is participating in a CLIR grant to digitize Western medieval and early modern manuscripts held by libraries in the greater Philadelphia area. The Library is lending thirteen medical manuscripts dating from c. 1220 to 1600 to this project, called Bibliotheca Philadelphiensis (BiblioPhilly). Our manuscripts will be digitized at the University of Pennsylvania’s Schoenberg Center for Electronic Text and Images (SCETI) and the digital images hosted through the University of Pennyslvania’s OPenn manuscript portal and dark-archived at Lehigh University.
